CoQ10 What Is It and How It Helps Lower Blood Pressure
You’re browsing the supplement aisle and keep seeing bottles labeled “CoQ10” with promises about heart health and energy. But what exactly is CoQ10? And can it really help with blood pressure like the labels claim?
If you’ve found yourself confused by all the different names – ubiquinol, ubiquinone, coenzyme Q10 – you’re not alone. Let’s clear up the confusion and show you what recent research says about this fascinating compound.
CoQ10: What Is It Really?
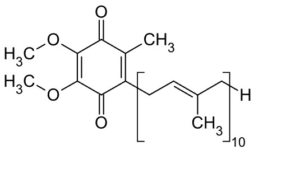
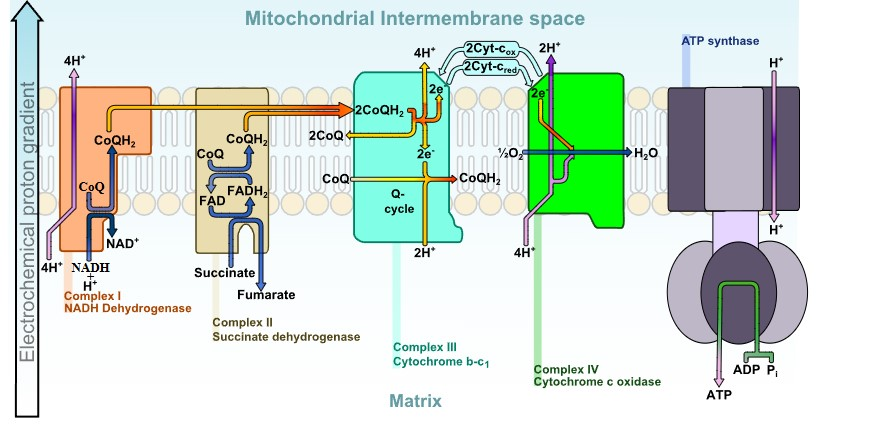
CoQ10 stands for Coenzyme Q10, and it’s one of the most important compounds you’ve probably never heard of. Think of CoQ10 as your cells’ energy factory manager – it helps convert the food you eat into usable energy.
Here’s what makes CoQ10 special: it’s found in almost every cell in your body, especially in organs that need lots of energy like your heart, liver, and kidneys. Your body makes CoQ10 naturally, but production starts declining after age 30.
The Two Forms: Ubiquinone vs. Ubiquinol
CoQ10 exists in your body in two main forms, and understanding the difference can help you choose the right supplement:
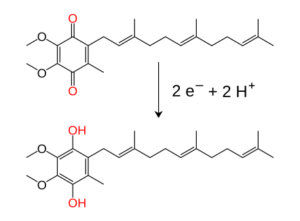
Ubiquinone (Oxidized Form)
• The original form of CoQ10
• More stable and shelf-stable
• Needs to be converted by your body
• Less expensive to produce
• Most research studies use this form
Ubiquinol (Reduced Form)
• The “active” form your body uses
• May be better absorbed, especially after age 40
• Ready to use immediately
• More expensive to manufacture
• About 95% of CoQ10 in your body is this form
A 2018 study found that ubiquinol was more effective than ubiquinone for increasing CoQ10 levels in older men, suggesting that as we age, our bodies become less efficient at converting ubiquinone to ubiquinol.
How CoQ10 Works in Your Body
To understand how CoQ10 helps with blood pressure, let’s look at what it actually does in your cells.
CoQ10’s Journey Through Your Body:
This process is particularly important for your cardiovascular system because your heart is one of the most energy-demanding organs in your body, beating over 100,000 times per day.
CoQ10 for Blood Pressure: What the Latest Research Shows
The evidence for CoQ10’s blood pressure benefits has been building for decades, but recent research has given us the clearest picture yet of how well it works.
The 2025 Breakthrough Study
A comprehensive 2025 analysis published in the International Journal of Cardiology looked at 45 randomized controlled trials involving nearly 2,000 people. The results were impressive:
While 3.4 mmHg might seem small, it’s actually quite meaningful. Even a 2 mmHg reduction in systolic blood pressure can reduce stroke risk by 6% and heart disease risk by 4%.
The Sweet Spot: Optimal Dosing
One of the most interesting findings from recent research is the U-shaped dose-response relationship with CoQ10. This means that both too little and too much can be less effective than the optimal middle range.
| Daily Dose | Blood Pressure Effect | Study Duration | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50-100mg | Mild reduction | 8+ weeks | Prevention, maintenance |
| 100-200mg | Maximum benefit | 8+ weeks | Most people with high BP |
| 200-400mg | Moderate benefit | 12+ weeks | Severe deficiency, heart conditions |
| 400mg+ | Diminishing returns | Variable | Specific medical conditions only |
Who Benefits Most from CoQ10?
The research shows that certain groups of people see particularly good results from CoQ10 supplementation:
People Who Respond Best to CoQ10:
- Adults over 40 (when natural CoQ10 production declines)
- People with diabetes or prediabetes
- Those with high cholesterol or taking statin medications
- Individuals with mild to moderate high blood pressure
- People with heart failure or other cardiovascular conditions
The 2025 research showed particularly strong benefits in people with diabetes and dyslipidemia, with some subgroups seeing blood pressure reductions of 6 mmHg or more.
How CoQ10 Compares to Other Natural Blood Pressure Approaches
CoQ10 is just one tool in the natural blood pressure management toolkit. Let’s see how it stacks up against other proven approaches:
| Approach | Blood Pressure Reduction | Time to Results | Monthly Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| CoQ10 supplements | 3-6 mmHg systolic | 8-12 weeks | $15-40 |
| Magnesium supplements | 2-4 mmHg systolic | 8-12 weeks | $10-25 |
| DASH diet | 5-11 mmHg systolic | 2-8 weeks | Variable |
| Regular exercise | 5-8 mmHg systolic | 4-8 weeks | Free-$50 |
| Weight loss (10 lbs) | 5-10 mmHg systolic | 8-16 weeks | Variable |
The real power comes from combining approaches. When you use CoQ10 along with other strategies like those found in comprehensive blood pressure management plans, the benefits often add up to more than any single approach alone.
Natural Food Sources vs. Supplements
Your body makes CoQ10 naturally, and you can also get small amounts from food. But here’s the reality: it’s nearly impossible to get therapeutic amounts from diet alone.
Foods That Contain CoQ10
Best Food Sources (per 3.5 oz serving):
- Beef heart: 11.3mg (highest natural source)
- Beef liver: 3.9mg
- Sardines: 2.0mg
- Chicken breast: 1.4mg
- Olive oil: 0.4mg
- Broccoli: 0.3mg
Even the richest food sources provide only 5mg or less of CoQ10, while the therapeutic range for blood pressure benefits is 100-200mg daily. This is why supplementation becomes necessary if you want to see cardiovascular benefits.
Choosing the Right Supplement
Not all CoQ10 supplements are created equal. Here’s what to look for:
For Most People
Ubiquinone (CoQ10):
• More affordable option
• Extensively researched
• Good for ages 20-40
• Look for 100-200mg doses
For Older Adults (40+)
Ubiquinol:
• Better absorption over age 40
• More bioavailable form
• Higher cost but may be worth it
• Look for 100-150mg doses
Maximizing Absorption
CoQ10 is fat-soluble, which means it needs fat to be absorbed properly. Here are tips for getting the most from your supplement:
- Take with meals: Especially meals containing some healthy fats
- Choose soft-gel capsules: These absorb better than hard tablets
- Split large doses: Take 100mg twice daily rather than 200mg once
- Be consistent: Take at the same time each day
- Be patient: Full benefits may take 8-12 weeks to develop
Safety and Side Effects
CoQ10 is remarkably safe for most people, with very few reported side effects even at high doses. Studies have used doses up to 1,200mg daily without serious adverse effects.
Mild Side Effects (Rare)
The most common side effects are mild and often resolve on their own:
- Mild stomach upset (take with food to minimize)
- Nausea (usually with doses over 300mg)
- Diarrhea (reduce dose if this occurs)
- Insomnia (take earlier in the day)
- Skin rash (very rare, stop if this occurs)
Important Drug Interactions
Talk to Your Doctor If You Take:
- Blood thinners like warfarin (CoQ10 may reduce effectiveness)
- Blood pressure medications (may enhance effects)
- Certain chemotherapy drugs
- Insulin or diabetes medications
While CoQ10 is generally safe, combining it with blood pressure medications might lower your blood pressure more than expected. This isn’t necessarily dangerous, but it should be monitored by your healthcare provider.
The Statin Connection: Why CoQ10 Matters More
If you’re taking statin medications for cholesterol, CoQ10 becomes even more important. Here’s why:
Statin drugs work by blocking an enzyme called HMG-CoA reductase, which your body uses to make cholesterol. But this same enzyme is also needed to produce CoQ10. So while statins effectively lower cholesterol, they also reduce your body’s natural CoQ10 production.
Many healthcare providers now recommend CoQ10 supplements for people taking statins, not just for blood pressure benefits but to help prevent muscle-related side effects.
CoQ10 Deficiency: Signs You Might Need More
Since CoQ10 is essential for cellular energy production, deficiency can show up in various ways:
Common Signs of Low CoQ10:
- Unexplained fatigue or low energy levels
- Muscle weakness or pain
- High blood pressure
- Poor exercise tolerance
- Gum disease or dental problems
- Frequent infections
These symptoms aren’t specific to CoQ10 deficiency, but if you have several of them along with risk factors (age over 40, statin use, poor diet), supplementation might help.
Getting Started: Your CoQ10 Action Plan
If you’re considering CoQ10 for blood pressure support, here’s a practical approach:
Tracking Your Progress
Keep a simple log of:
- Daily CoQ10 dose and timing
- Blood pressure readings (same time of day)
- Energy levels (1-10 scale)
- Any side effects
- Other supplements or medications
The Future of CoQ10 Research
Research into CoQ10 continues to evolve, with scientists exploring several exciting areas:
- Personalized dosing: Using genetic testing to determine optimal CoQ10 doses
- Enhanced absorption: New delivery methods to improve bioavailability
- Combination therapies: Testing CoQ10 with other natural compounds
- Prevention applications: Using CoQ10 to prevent cardiovascular disease in healthy people
Making Sense of the Marketing Claims
You’ll see many bold claims about CoQ10 in supplement marketing. Let’s separate fact from fiction:
Questionable Claims
• “Instant energy boost”
• “Miracle heart cure”
• “Fountain of youth”
• “Works for everyone”
• “No side effects possible”
Evidence-Based Benefits
• Modest blood pressure reduction
• Improved heart function in some conditions
• Antioxidant protection
• Potential energy support over time
• Well-tolerated by most people
The Bottom Line on CoQ10
CoQ10 is a well-researched, generally safe supplement that can provide modest but meaningful blood pressure benefits for many people. It’s not a miracle cure, but it’s a legitimate tool in the natural health toolkit.
The 2025 research gives us confidence that CoQ10 can help lower blood pressure, especially when used consistently at the right dose (100-200mg daily) for an adequate duration (8+ weeks).
Whether you choose ubiquinone or ubiquinol, the most important factors are consistency, proper dosing, and patience. Like most natural approaches, CoQ10’s benefits build over time rather than providing instant results.
If you’re over 40, take statin medications, or have cardiovascular risk factors, CoQ10 supplementation makes particular sense. Even if you’re younger and healthy, the antioxidant and cellular energy benefits may support long-term cardiovascular health.
Start with a quality supplement, track your progress, and give it at least 12 weeks to show its full potential. Your heart – and your blood pressure numbers – may thank you for it.
some really good research that is related to this whole subject can be watched here.. warning this is 1 hour long video
References
- PMC. “Effects of coenzyme Q10 administration on blood pressure and heart rate in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.” International Journal of Cardiology, 2025.
- ScienceDirect. “Dose-Response Effect of Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation on Blood Pressure among Patients with Cardiometabolic Disorders.” 2022.
- Today’s Practitioner. “Coenzyme Q10 (Ubiquinol) and Hypertension: Effects on Blood Pressure and Cardiovascular Health.” August 2025.
- Swanson Vitamins. “Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) & Ubiquinol: What’s the Difference?”
- PubMed. “Ubiquinol is superior to ubiquinone to enhance Coenzyme Q10 status in older men.” November 2018.
- WebMD. “What Are the Benefits and Side Effects of CoQ10 (Coenzyme Q10)?”
- International Journal of Endocrinology. “Coenzyme Q10: A Key Antioxidant in the Management of Diabetes‐Induced Cardiovascular Complications.” March 2024.
- PMC. “Dose-Response Effect of Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation on Blood Pressure among Patients with Cardiometabolic Disorders.”
- Mayo Clinic. “Coenzyme Q10.” May 2025.
- PMC. “Comparison of Coenzyme Q10 (Ubiquinone) and Reduced Coenzyme Q10 (Ubiquinol) as Supplement to Prevent Cardiovascular Disease.”
- Healthline. “9 Benefits of Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10).” September 2024.
- Nature Made. “Ubidecarenone vs. Ubiquinol: CoQ10 Guide.” May 2024.
Medical Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and doesn’t constitute medical advice. High blood pressure is a serious medical condition that requires professional supervision. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider before starting any new supplements, especially if you take medications or have underlying health conditions. CoQ10 may interact with certain medications, particularly blood thinners and blood pressure medications. Individual results may vary, and this information shouldn’t replace professional medical guidance.
Author Bio: The Remedy Verified Team translates complex metabolic science into clear, practical strategies for everyday health.