Magnesium Supplement for Blood Pressure: What Science Really Shows
You’re standing in the supplement aisle, looking at rows of magnesium bottles. The labels promise better blood pressure, but you’re wondering: does this mineral really work, or is it just expensive hope in a bottle?
Here’s the straight answer: magnesium supplements can help lower blood pressure, but the effect is modest. A major 2024 research review found that people who took magnesium supplements saw their blood pressure drop by an average of 1.4 mmHg. That might not sound like much, but it can make a real difference for your heart health.
How Magnesium Lowers Your Blood Pressure
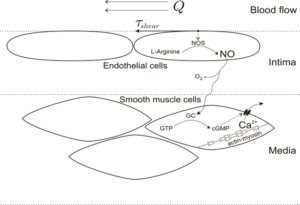
Think of magnesium as your blood vessels’ relaxation coach. This mineral works in several ways to help keep your blood pressure in check.
First, magnesium acts like a natural calcium channel blocker. Calcium makes your blood vessels tighten up, while magnesium tells them to relax. It’s like having someone massage tense shoulders – the vessels loosen up, and blood flows more easily.
Magnesium also boosts nitric oxide production in your body. Nitric oxide is like a “chill out” signal for your blood vessels, helping them stay flexible and open.
Here’s How Magnesium Works in Your Body:
Plus, magnesium helps your kidneys manage sodium better. When you have enough magnesium, your body doesn’t hold onto as much salt, which also helps keep blood pressure down.
The Latest Research: What 2024 Studies Reveal
The most comprehensive research on magnesium and blood pressure came out in 2024. Scientists looked at data from over 8,600 people who took part in various magnesium studies.
Now, you might think those numbers seem small. But here’s why they matter: even a 2 mmHg drop in blood pressure can reduce your risk of heart disease by about 6% and stroke risk by 8%.
The research showed that magnesium works best when you:
- Take at least 400mg per day
- Use it for 12 weeks or longer
- Already have high blood pressure or other health issues
- Combine it with other heart-healthy habits
Who Gets the Biggest Benefits?
The studies found that certain people see much better results from magnesium supplements than others.
| Group | Average Blood Pressure Drop | Why It Works Better |
|---|---|---|
| People with diabetes | 4.2/2.3 mmHg | Often have low magnesium levels |
| Those with insulin resistance | 4.2/2.3 mmHg | Magnesium improves insulin function |
| Adults over 60 | 3-5 mmHg systolic | Age-related magnesium deficiency |
| People taking certain medications | 2-4 mmHg | Some drugs deplete magnesium |
One 2021 study found that magnesium works even better when your blood pressure isn’t well controlled. People not taking blood pressure medications saw benefits at 600mg daily, while those already on medications needed only 240mg daily to see improvements.
Are You Getting Enough Magnesium?
Here’s something that might surprise you: up to 15% of Americans don’t get enough magnesium from their diet. This deficiency often flies under the radar because most doctors don’t test for it in regular blood work.
Signs You Might Be Low on Magnesium
Magnesium deficiency can be sneaky. Early signs are often vague and easy to blame on other things:
Common Early Signs:
- Muscle cramps or twitches (especially at night)
- Feeling tired even when you get enough sleep
- Trouble falling asleep or staying asleep
- Feeling more anxious or stressed than usual
- Headaches that come and go
- Heart palpitations or irregular heartbeat
Who’s Most at Risk for Low Magnesium?
Certain people are more likely to have low magnesium levels:
- Older adults: We absorb less magnesium as we age
- People with diabetes: High blood sugar makes you lose magnesium through urine
- Those taking certain medications: Proton pump inhibitors, diuretics, and some antibiotics
- Heavy drinkers: Alcohol interferes with magnesium absorption
- People with digestive issues: Conditions like Crohn’s disease or celiac disease
How Much Magnesium Should You Take?
The “right” dose of magnesium depends on your age, health status, and what you’re trying to achieve.
For blood pressure benefits, research suggests these amounts work best:
| Goal | Daily Dose | Duration | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| General heart health | 300-400mg | Ongoing | Good starting point for most people |
| Blood pressure support | 400-500mg | 12+ weeks | Most effective dose range |
| Diabetes/insulin resistance | 400-600mg | 12+ weeks | May need higher amounts |
| Deficiency correction | 200-400mg | 8-12 weeks | Start lower, increase gradually |
The FDA’s recommended daily amount is much lower – just 400mg for men and 310mg for women. But many experts think these amounts are too low for optimal health benefits.
Timing Matters Too
When you take magnesium can affect how well it works:
- With meals: Reduces stomach upset and improves absorption
- Evening: Can help with sleep quality (bonus benefit!)
- Spread out: If taking large doses, split them throughout the day
- Away from other supplements: Calcium and magnesium can compete for absorption
Types of Magnesium: Which One’s Best for Blood Pressure?

Walk into any supplement store, and you’ll see dozens of different magnesium types. Each one has different properties and absorption rates.
Best for Blood Pressure
Magnesium Glycinate: Easily absorbed, gentle on stomach, well-studied for heart health
Magnesium Taurate: Combined with taurine for extra cardiovascular support
Budget-Friendly Options
Magnesium Citrate: Good absorption, affordable, also helps with constipation
Magnesium Malate: Well-absorbed, may help with energy levels
Forms to Avoid for BP
Magnesium Oxide: Cheap but poorly absorbed (only 10% gets into your system). Mainly useful as a laxative.
Here’s a breakdown of what the research shows:
| Type | Absorption Rate | Best For | Potential Downsides |
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnesium Glycinate | High (90%+) | Blood pressure, sleep, anxiety | More expensive |
| Magnesium Citrate | Good (80%) | BP support, constipation | Can cause loose stools |
| Magnesium Taurate | Good (80%) | Heart health, blood pressure | Limited research |
| Magnesium Oxide | Poor (10%) | Constipation relief only | Not effective for BP |
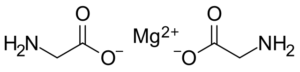
Magnesium vs. Other Natural Blood Pressure Helpers
You might wonder how magnesium stacks up against other natural approaches to blood pressure. Let’s put it in perspective:
Magnesium Supplements
• Drop: 1-4 mmHg
• Works in: 8-12 weeks
• Cost: $10-30/month
• Side effects: Minimal
Potassium Supplements
• Drop: 2-3 mmHg
• Works in: 4-8 weeks
• Cost: $15-25/month
• Side effects: Can be dangerous with some meds
The exciting thing is that these natural approaches work even better when you combine them. Research shows that taking magnesium along with potassium and reducing sodium can lower blood pressure as much as some medications.
This is why comprehensive approaches like the DASH diet and proven blood pressure supplements are so effective – they address multiple pathways at once.
Can You Get Enough Magnesium from Food?
Ideally, you’d get all your magnesium from a balanced diet. Some foods are packed with this mineral:
Top Magnesium-Rich Foods:
- Almonds: 1 ounce = 80mg magnesium (20% daily value)
- Spinach: 1 cup cooked = 160mg magnesium
- Black beans: 1 cup = 120mg magnesium
- Dark chocolate: 1 ounce = 65mg magnesium
- Avocado: 1 medium = 58mg magnesium
- Whole grains: 1 cup brown rice = 84mg magnesium
- check out this potassium-rich foods in the DASH eating plan PDF
But here’s the reality: most people don’t eat enough of these foods consistently. Plus, modern farming practices have reduced the magnesium content in many foods compared to decades ago.
That’s where supplements can bridge the gap. Think of them as insurance for your heart health, especially if you’re trying to manage blood pressure naturally.
Safety and Side Effects: What You Need to Know
Magnesium supplements are generally very safe for most people. Unlike some other supplements, it’s hard to take too much because your kidneys are good at getting rid of excess amounts.
Common Side Effects (Usually Mild)
- Loose stools or diarrhea: The most common side effect, especially with higher doses
- Stomach upset: Usually goes away when taken with food
- Nausea: More likely on an empty stomach
Who Should Be Careful?
While magnesium is safe for most people, certain situations require extra caution:
Talk to your doctor first if you:
- Take blood pressure medications (magnesium can enhance their effects)
- Have kidney disease (your body may not eliminate excess magnesium properly)
- Take antibiotics, diuretics, or proton pump inhibitors
- Have heart rhythm problems
- Are pregnant or breastfeeding
Drug Interactions to Watch
Magnesium can interact with several medications:
| Medication Type | Interaction | What to Do |
|---|---|---|
| Blood pressure meds | May lower BP too much | Monitor BP closely with doctor |
| Antibiotics | Reduces antibiotic absorption | Take 2+ hours apart |
| Diuretics | Can cause low magnesium | May need higher magnesium dose |
| Calcium supplements | Compete for absorption | Take at different times |
Building Your Magnesium Strategy
So you’ve decided to try magnesium for blood pressure support. Here’s how to do it smart:
Maximizing Your Results
Magnesium works better when it’s part of a comprehensive approach:
- Eat magnesium-rich foods: Supplements plus food sources work better together
- Reduce sodium: Less salt means magnesium can work more effectively
- Stay hydrated: Proper hydration supports magnesium function
- Manage stress: Chronic stress depletes magnesium levels
- Get quality sleep: Magnesium can help, and good sleep supports heart health
When to Expect Results
If you’re thinking about trying magnesium, here’s a realistic timeline of what to expect:
First Week
You probably won’t notice blood pressure changes yet, but you might sleep better or feel less anxious. Some people report fewer muscle cramps.
2-4 Weeks
Your body’s magnesium levels start to improve. You might notice subtle improvements in energy and mood.
8-12 Weeks
This is when most studies see blood pressure benefits. If you’re tracking your numbers at home, you might start seeing modest improvements.
3 Months and Beyond
Full benefits become apparent. Blood pressure improvements tend to be sustained with continued use.
The FDA’s Take on Magnesium and Blood Pressure
In 2022, the FDA made an interesting decision. They allowed supplement companies to make health claims about magnesium and blood pressure, but with an important caveat.
The FDA requires companies to include language stating that the evidence is “inconclusive and inconsistent.” What does this mean for you?
- The research shows promise, but it’s not as strong as we’d like
- Results vary significantly between people
- More research is needed to establish clearer guidelines
- It’s not a replacement for proven treatments
This doesn’t mean magnesium doesn’t work – it just means the science is still evolving, and individual responses vary a lot.
Cost-Effectiveness: Is Magnesium Worth It?
Let’s talk money. Magnesium supplements typically cost $10-30 per month, depending on the type and brand you choose.
Compare that to:
- Blood pressure medications: $20-200+ per month
- Doctor visits for BP management: $150-300 each
- Long-term costs of untreated high blood pressure: thousands
Even if magnesium only provides modest benefits, it’s one of the most affordable approaches to comprehensive blood pressure management.
Common Mistakes People Make with Magnesium
After researching thousands of magnesium studies, here are the biggest mistakes I see people make:
What Doesn’t Work
• Taking magnesium oxide (poor absorption)
• Expecting immediate results
• Taking too much too quickly
• Ignoring other BP factors
What Works Better
• Choosing well-absorbed forms
• Starting slowly and building up
• Combining with other healthy habits
• Being consistent for 3+ months
The Bottom Line: Should You Try Magnesium?
Based on current research, magnesium supplements can be a helpful addition to your blood pressure management strategy. They won’t replace medications if you need them, but they might help reduce your overall cardiovascular risk.
Magnesium makes the most sense if you:
- Have mildly elevated blood pressure (130-150 mmHg)
- Are looking for natural approaches to support heart health
- Have diabetes or insulin resistance
- Don’t get much magnesium from your diet
- Want an affordable, low-risk intervention
The research is clear: magnesium won’t dramatically transform your blood pressure overnight. But for many people, it can provide modest, sustained benefits that add up to meaningful improvements in cardiovascular health over time.
Plus, magnesium offers bonus benefits like better sleep, reduced stress, and improved energy – making it one of the more well-rounded supplements you can take for overall health.
If you decide to try magnesium, start with a well-absorbed form like magnesium glycinate, begin with a modest dose, and give it at least 12 weeks to show its effects. Track your blood pressure regularly and work with your healthcare provider to monitor your progress.
Your heart will thank you for taking a comprehensive approach to blood pressure management that includes both proven medical treatments and safe, evidence-based natural support like magnesium.
References
- ScienceDirect. “Impact of Magnesium Supplementation on Blood Pressure: An Umbrella Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.” July 2024.
- Zhang, X., et al. “Effects of Magnesium Supplementation on Blood Pressure: A Meta-Analysis.” Hypertension, 2016.
- PMC. “The effect of magnesium supplementation on blood pressure in individuals with insulin resistance, prediabetes, or noncommunicable chronic diseases.”
- Harvard Health Publishing. “Magnesium and blood pressure: What’s the evidence?” April 2022.
- Healthline. “Magnesium Deficiency: Symptoms, Recommendations, and More.” December 2024.
- University of Nebraska Health Center. “8 magnesium deficiency symptoms (and 9 high magnesium foods).”
- Cleveland Clinic. “Hypomagnesemia: What It Is, Causes, Symptoms & Treatment.” June 2025.
- University Hospitals. “Which Type of Magnesium Is Right for Your Symptoms?” April 2025.
- GoodRx. “Magnesium and Blood Pressure: What Is the Connection?” May 2023.
- PMC. “The Role of Magnesium in Hypertension and Cardiovascular Disease.”
- WebMD. “MAGNESIUM: Overview, Uses, Side Effects, Precautions, Interactions, Dosing and Reviews.”
- MedlinePlus. “Magnesium Blood Test: MedlinePlus Medical Test.”
Medical Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and doesn’t constitute medical advice. High blood pressure is a serious medical condition that requires professional supervision. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider before making changes to your blood pressure management plan, starting new supplements, or adjusting medications. Individual results may vary, and this information shouldn’t replace professional medical guidance.
Author Bio: The Remedy Verified Team translates complex metabolic science into clear, practical strategies for everyday health.
“Magnesium rich foods” image © respective author, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons. Link to file page.
“Magnesium glycinate supplement Australia.jpg” CC0 Public Domain (no attribution required).
“Magnesium diglycinate structural formula” Public Domain (PD-chem).
“EDRF regulation diagram” CC BY-SA 3.0.
“Korotkow-sound-principle.svg” Public Domain.
NHLBI DASH chart Public Domain (U.S. gov). NHLBI, NIH
Video (YouTube “Hypertension | Vital Signs”) CC BY 3.0 — attribute the channel + video title with a link.